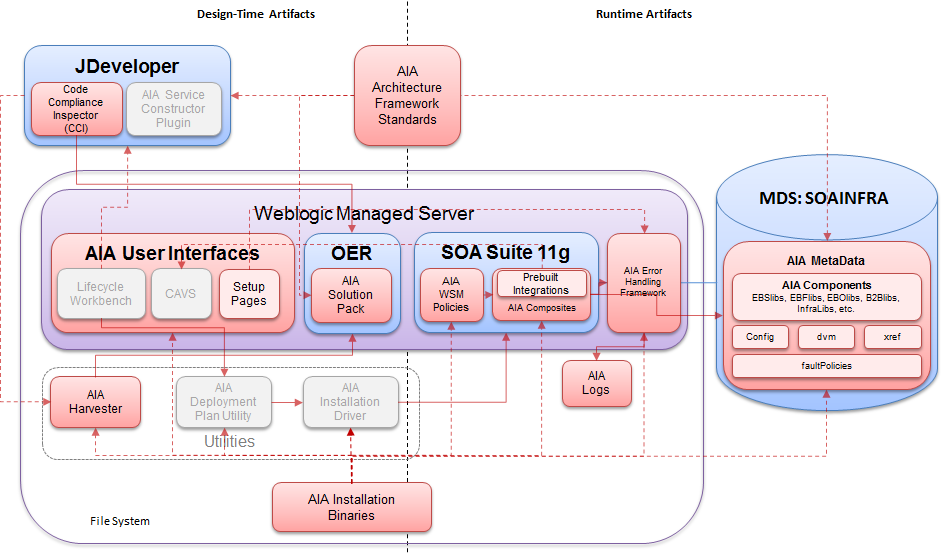
AIA Foundation Pack Architecture Overview
The Oracle Application Integration
Architecture Foundation Pack (recently renamed to just Foundation Pack) at is
Oracle's accelerator framework for implementing SOA-based system integrations.
AIA FP and its prebuilt integrations such as PIPs were originally created to
facilitate and accelerate the integration between different Oracle applications
such as Siebel, E-Business Suite, PeopleSoft, and JD Edwards, among others.
Customers looking to simultaneously implement and integrate several Oracle
applications gain huge benefits from employing PIPs, as these significantly
reduce the effort and risk involved with building interfaces to support
business processes. Given Oracle's aggressive and continuous growth by acquisition,
AIA FP and prebuilt integrations have become fundamental to rapidly integrate
newly acquired products with their existing apps portfolio.
The AIA FP contains a variety of
design-time and runtime artifacts that can be used when defining, designing,
building, testing, and deploying SOA solutions. The following diagram presents
an overview of the different components that build up the AIA FP:
The AIA FP consists of:
·
AIA Architecture Framework
Standards
·
Service Constructor JDeveloper
Plugin
·
Code Compliance Inspector (CCI)
·
Lifecycle Workbench
·
Composite Application
Validation System (CAVS)
·
Setup Pages
·
AIA Message Resubmission
Utility
·
AIA Solution Pack
·
AIA Harvester
·
AIA Deployment Plan Generator
·
AIA Installation Driver
·
AIA WSM Policies
·
AIA Composites
·
AIA Prebuilt Integrations
·
AIA Error Handling Framework
·
AIA Metadata
The preceding components will be
described in the following sections.
Design-time Artifacts
These artifacts include tools, libraries,
and other AIA assets that support the design-time phase of a project. These
tools are:
·
AIA
Architecture Framework Standards: Consists of
artifacts available for use during design-time governance stages. These include
a reference architecture, a methodology, reference process models, conventions,
and the AIA object library, which is basically a collection of XML artifacts
such as XSD's and WSDLs, available for use.
·
Service
Constructor JDeveloper Plugin: JDeveloper plugin
used to automate the creation of AIA services. At present this plugin only
supports the creation of AIA Business Connector
Services (ABCS)
INSERT IMAGE 9083EN_10_04.png
·
Code
Compliance Inspector (CCI):
JDeveloper plugin that can be used to check that code in SOA projects is
compliant with AIA standards and best practices.
·
AIA
User Interfaces: A number of web applications
aimed at supporting a project through the different AIA development lifecycle
phases. The main web applications are:
·
Lifecycle
Workbench: This application provides a
comprehensive console that can be used by business analysts, solution
architects, and services designers, to streamline the analysis, definition, and
decomposition of SOA solutions built with AIA.
·
CAVS: The Composite Application Validation
System (CAVS) is a testing application
that supports the creation of stub services to simulate back end systems that
might be unavailable during early testing stages. CAVS provides a mechanism for
services created in accordance with the AIA standards to programmatically route
a payload to CAVS, without the modification of the composite itself.
·
Setup
Pages: Basically a configuration page to set up
error notifications, error codes, routing configurations, and application
registries, among others.
·
AIA Message Resubmission Utility: It allows
browsing through a list of faults and resubmit them based on specific criteria:
INSERT IMAGE 9083EN_10_05.png
·
AIA
Solution Pack: This pack seeds OER with all of
the asset types, categorizations and metadata required to fully govern AIA
solutions and assets.
·
AIA
Utilities: A series of utilities available for
post installation use with the AIA FP. The main utilities are:
·
AIA
Harvester: A command line utility tailored for
harvesting AIA services and assets into OER.
·
AIA
Deployment Plan Generator: An Ant utility that
takes the Bill of Materials file (BOM.xml), generated from the Project Lifecycle Workbench pack, as input and
generates a Deployment Plan file (<projectCode>DP.xml) and a Harvester Settings file (HarvesterSettings.xml), based on the
information supplied in the BOM.
·
AIA
Installation Driver: An Ant utility that reads a
deployment plan generated from the Deployment Plan Generator and deploys all
SOA artifacts specified in the plan to the target servers contained in the
installation driver properties file (AIAInstallProperties.xml).
Runtime Artifacts
These artifacts include tools, libraries,
and other AIA assets that support the runtime phases of a project. The
supporting tools include:
·
AIA
WSM Policies: A Web
Service Manager policy set created by the AIA FP installer to globally
attach security policies to any AIA composite deployed to a SOA server.
·
AIA
Composites: A number of SOA Suite 11g AIA
composites deployed into the SOA Server. These include: AIA utility services
deployed during the AIA FP installation, AIA Prebuilt Integrations, and custom
developed AIA services that follow the AIA FP lifecycle. The following
screenshot shows the AIA composites deployed after installation of the FP:
·
AIA
Prebuilt Integrations: Prebuilt integration
solutions created by Oracle with the AIA FP. There are two types of Prebuilt
Integrations:
·
Direct
Integrations: Basically point-to-point
integrations that manage data flows and data synchronizations between
applications.
·
Process
Integration Packs (PIPs):
Integration accelerators that combine one or more integration styles, such as
data-centric integration, web services, reference data query, and/or
process-centric integrations, to deliver end-to-end integration solutions.
·
AIA
Error Handling Framework: This provides a
complete common error handling solution for services developed following the
AIA standards. As can be appreciated from the figure, the main features of the
AIA Error Handling framework are:
- Support for other technologies such as Oracle Data Integrator (ODI) and Oracle B2B
- Support for the main types of faults, such as system, remote, and business faults
- Configurable error notifications
- Integration with Human Workflow using the SOA/BPM Suite Worklist Application
- AIA specific error logger
·
AIA
Metadata: A set of XML artifacts that mainly
consist of AIA specific XSDs, WSDLs, and other XML files, that are stored in
the SOA Suite Metadata Service repository (MDS). The principle component of the AIA Metadata is
the AIA Components. AIA Components contains the
main XML libraries available for used in AIA FP. Enterprise
Business Object(s) (EBO) and Enterprise Business Message(s) (EBM) are examples of AIA XSDs available for use in the
object libraries. Enterprise Business Service(s)
(EBS) is an example of AIA WSDLs Assets
available for use in the service libraries.
For more information on AIA Foundation Pack you may refer to my book "Oracle SOA Governance 11g Implementation" which includes a chapter fully dedicated to this topic and includes a sample use case based on real live experience. Book is available in the following link or any other major book store.
http://www.packtpub.com/oracle-soa-governance-11g-implementation/book
For more information on AIA Foundation Pack you may refer to my book "Oracle SOA Governance 11g Implementation" which includes a chapter fully dedicated to this topic and includes a sample use case based on real live experience. Book is available in the following link or any other major book store.
http://www.packtpub.com/oracle-soa-governance-11g-implementation/book

Comments
Post a Comment